In the realm of lighting technology, Chip on Board (COB) LEDs have emerged as a revolutionary breakthrough, captivating engineers, designers, and enthusiasts alike. But how do these tiny powerhouses of light actually work? Let’s delve into the inner workings of COB LEDs to unravel the magic behind their brilliance.
Exploring the Inner Workings of COB LED Chips
At the heart of a COB LED lies a densely populated cluster of individual LED chips mounted directly onto a substrate. This ingenious design eliminates the need for individual encapsulation, allowing for an intimate arrangement of diodes. Picture this: a multitude of miniature light emitters grouped closely together, all integrated onto a single board.
Each of these tiny diodes produces its own stream of photons when an electric current is applied. By aggregating numerous LEDs, COB technology generates an intense and focused beam of light. This clustered configuration accounts for the impressive luminosity and uniformity that COB LEDs are celebrated for.
Furthermore, the substrate itself plays a crucial role in the COB LED’s performance. Often constructed from materials with high thermal conductivity, like ceramic or metal, the substrate aids in efficient heat dissipation. This is paramount for sustaining the LED’s longevity and preventing overheating, a concern in high-powered applications.
Comparing COB LEDs to SMD LEDs
To appreciate the unique attributes of COB LEDs, it’s valuable to contrast them with their Surface Mount Device (SMD) counterparts.
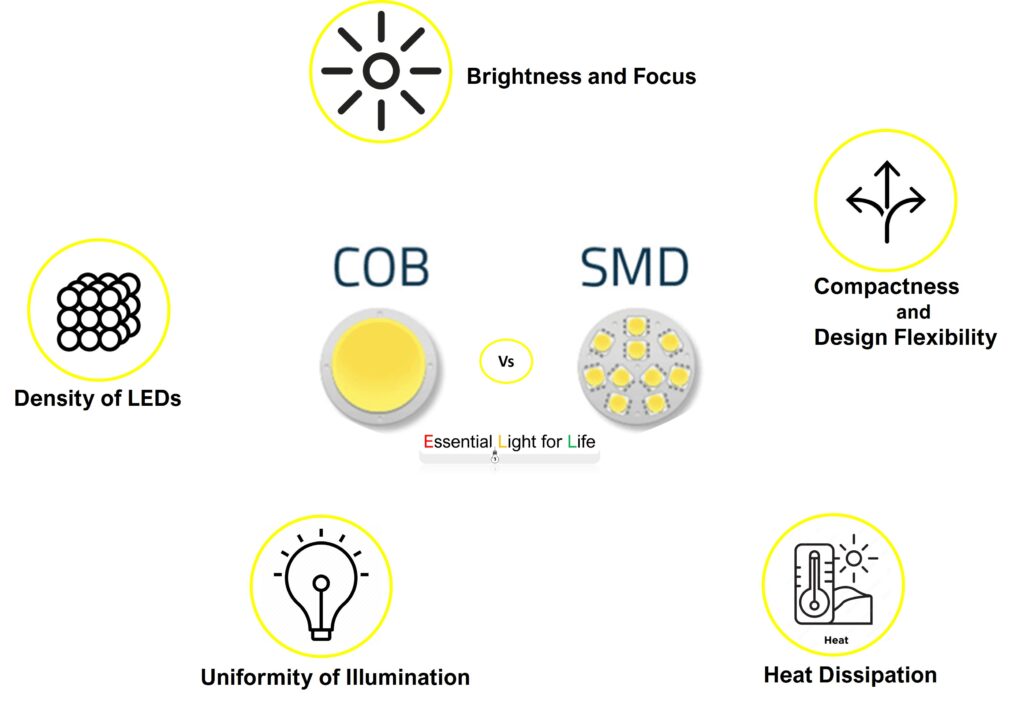
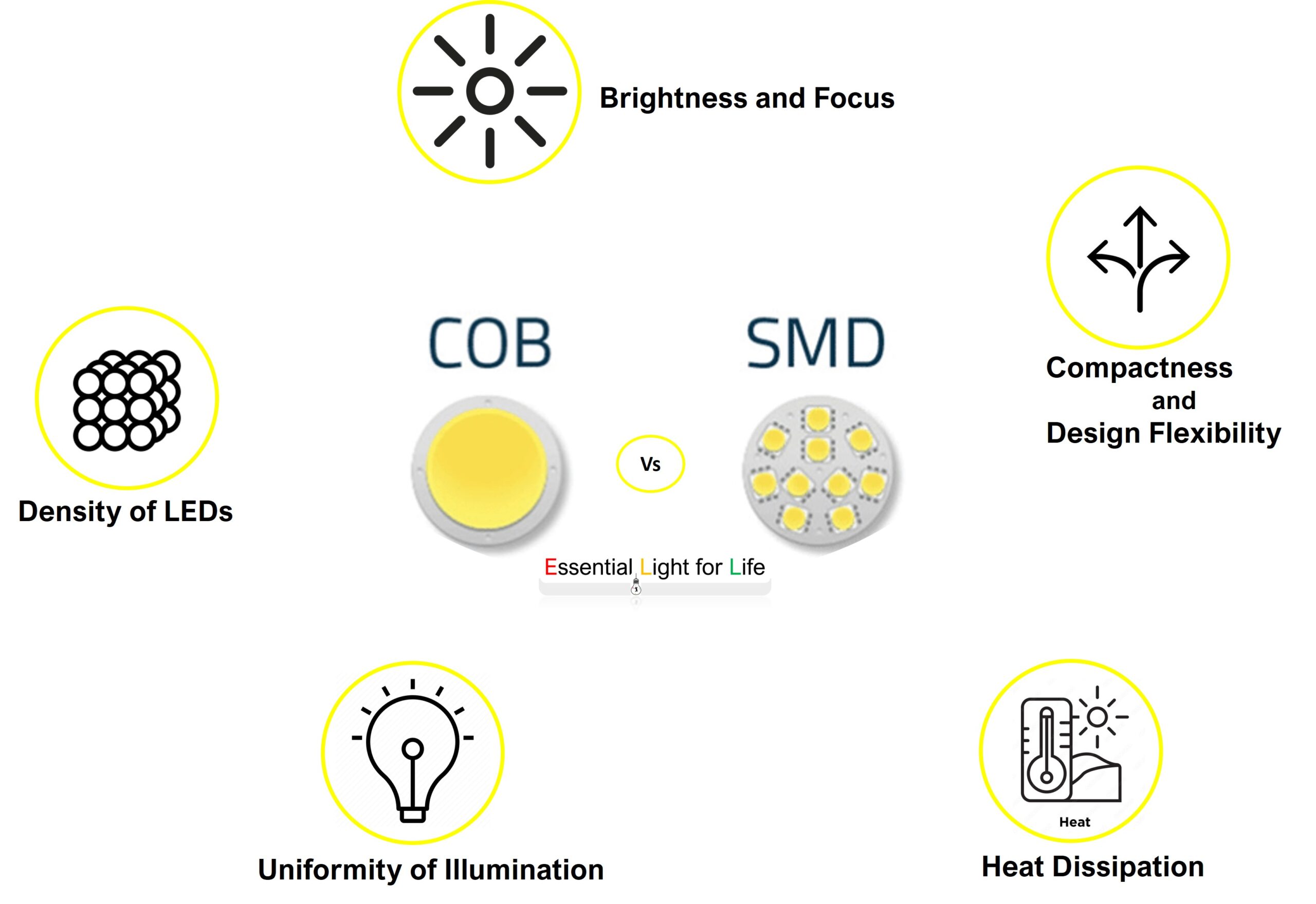
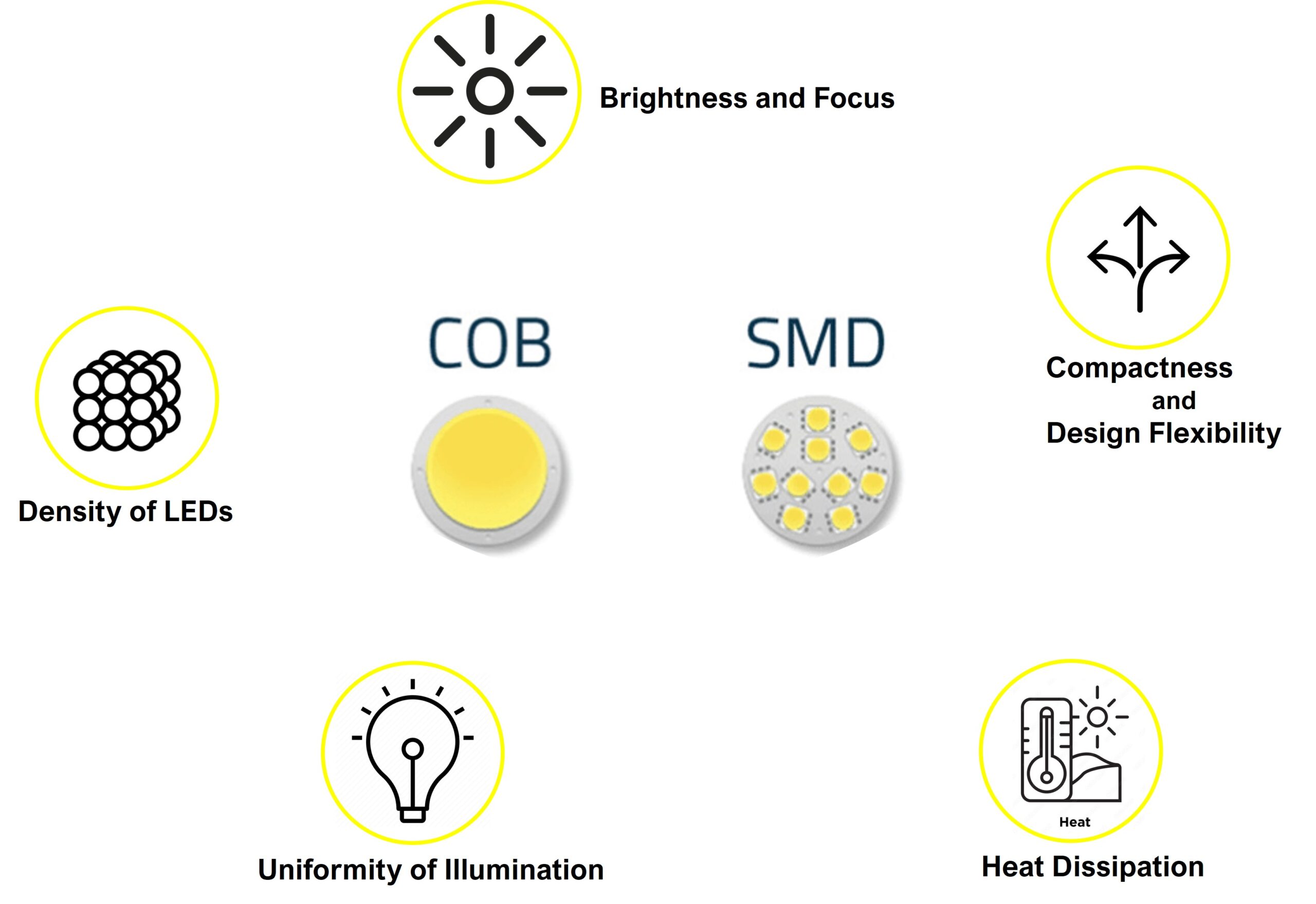
- Density of LEDs: In SMD LEDs, individual diodes are encapsulated in a small plastic package, leading to some degree of space between each LED. COB LEDs, on the other hand, feature LEDs mounted directly onto the substrate, allowing for a higher LED density.
- Uniformity of Illumination: Due to their densely packed configuration, COB LEDs produce a remarkably even distribution of light, reducing the appearance of multiple shadows. SMD LEDs may exhibit slight variations in illumination across their surface.
- Heat Dissipation: COB LEDs benefit from the integrated design, which enhances thermal management. This minimizes the risk of overheating and extends the LED’s lifespan. SMD LEDs, with their discrete packaging, may necessitate additional heat sinks or cooling measures.
- Brightness and Focus: COB LEDs are adept at producing high-intensity, focused light beams, making them ideal for applications where brightness and precision are paramount. SMD LEDs are versatile but may not achieve the same level of intensity.
- Compactness and Design Flexibility: COB LEDs’ integrated design allows for sleeker, more streamlined luminaire designs. SMD LEDs, with their individual packaging, may require more space.
In the grand tapestry of lighting technology, COB LEDs stand as a testament to innovation, delivering high-powered, uniform illumination in a compact and efficient form. Their ingenious design and impressive performance make them a game-changer in various industries, from automotive to horticulture, and from architectural to theatrical lighting.